Building credit at 18 is a crucial step toward financial independence and stability. Establishing a strong credit foundation early on can set you up for success in many areas of life, from securing loans at better interest rates to renting an apartment or even landing your dream job. Let’s explore some practical and effective strategies on how to start building credit at 18, to help you get started on the right foot.
Learn how to Start Building Credit at 18
1. Understanding Credit
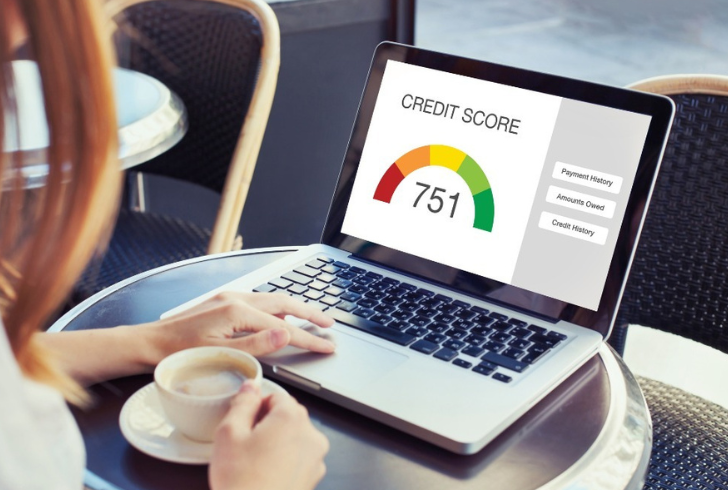

Instagram | smithproulxteam | Your credit report, managed by major bureaus, influences your credit score greatly.
Your credit report, which is maintained by the three major credit reporting bureaus—Experian™, Equifax®, and TransUnion®—plays a pivotal role in determining your credit score. This score, which lenders use to assess your creditworthiness, is calculated using models like VantageScore 3.0® and FICO®.
Key Factors Influencing Your Credit Score
There are several factors that contribute to your credit score:
- Payment History: Consistently paying your bills on time.
- Credit Utilization: The ratio of your credit card balances to your credit limits.
- Length of Credit History: The age of your credit accounts.
- Credit Mix: The variety of credit accounts you have, such as credit cards, loans, etc.
- New Credit: Recent credit inquiries and newly opened accounts.
Free Credit Reports
You are entitled to a free credit report from each of the major bureaus once a year. This report helps you monitor your credit health and understand how future lenders might view your financial behavior. A strong credit score can lead to lower interest rates on loans and credit cards, saving you money in the long run.
2. Becoming an Authorized User
Leveraging an existing credit line can jumpstart your credit journey! Becoming an authorized user on a parent's or responsible friend's credit card allows you to benefit from their positive payment history. But remember, this is a two-way street: their spending habits will impact your score, so choose wisely.
Before diving in, have an open conversation to set clear expectations and ensure the credit card company reports authorized user activity, otherwise your credit score won't budge.
3. Getting Your First Credit Card
A credit card is a powerful tool for building credit when used responsibly. If you’re new to credit, consider starting with a student credit card or a secured credit card.
- Student Credit Cards - These cards are designed for college students with little to no credit history. They often have lower credit limits and fewer rewards but can be a great starting point.
- Secured Credit Cards - A secured credit card requires a cash deposit, which serves as collateral. Your credit limit is usually equal to the deposit amount. Using a secured credit card responsibly can help you establish credit and eventually qualify for an unsecured card.
4. Timely Payments

Instagram | user18526052 | Timely bill payments are crucial for a healthy credit score.
Paying your bills on time is one of the most important aspects of building and maintaining a good credit score. This includes not only credit card bills but also other financial obligations like car loans and student loans.
Tips for Ensuring Timely Payments
- Autopay: Set up automatic payments to avoid missing due dates.
- Reminders: Use calendar alerts or apps to keep track of payment schedules.
- Budgeting: Plan your finances to ensure you have enough funds to cover your bills each month.
5. Managing Credit Utilization
Your credit utilization ratio, or the amount of credit you’re using compared to your total available credit, is a significant factor in your credit score. Aim to keep this ratio below 30%, and ideally closer to 10%.
To manage this, focus on paying your balance in full each month to avoid interest and consider making multiple small payments throughout the month. If you're disciplined, requesting a credit limit increase can also lower your utilization ratio, but remember, it shouldn't be an excuse to overspend!
6. Considering Student Loans

Freepik | Obtaining a student loan can diversify your credit mix and establish a credit history.
Taking out a student loan can be another way to build credit. While loans can contribute to your credit mix and help build your credit history, it's important to borrow responsibly and make timely payments once the repayment period begins.
Loan Options
- Federal Loans: Often have lower interest rates and flexible repayment options.
- Private Loans: Can be used to fill gaps in funding but usually have higher interest rates.
- Refinance: Refinancing can lower your interest rate and reduce monthly payments.
7. Monitoring Your Credit
Once you start building credit, it's vital to keep an eye on your credit report and score. Tools like Chase Credit Journey offer free access to your credit score and alerts for any changes or inaccuracies.
Steps for Effective Monitoring
- Regular Checks: Review your credit report periodically to ensure all information is accurate.
- Report Errors: If you find any discrepancies, report them to the credit bureaus immediately.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with changes in your credit score to understand how your actions impact your credit health.
Learning how to start building credit at 18 is a significant step towards financial independence. By following these steps and using credit responsibly, you'll be well on your way to unlocking a world of financial opportunities!